Oligomers count
attyloid’s sFIDA platform technology offers a cutting-edge approach for the quantitative detection of single oligomers and aggregates, which serve as biomarkers of CNS disorders such as Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease.
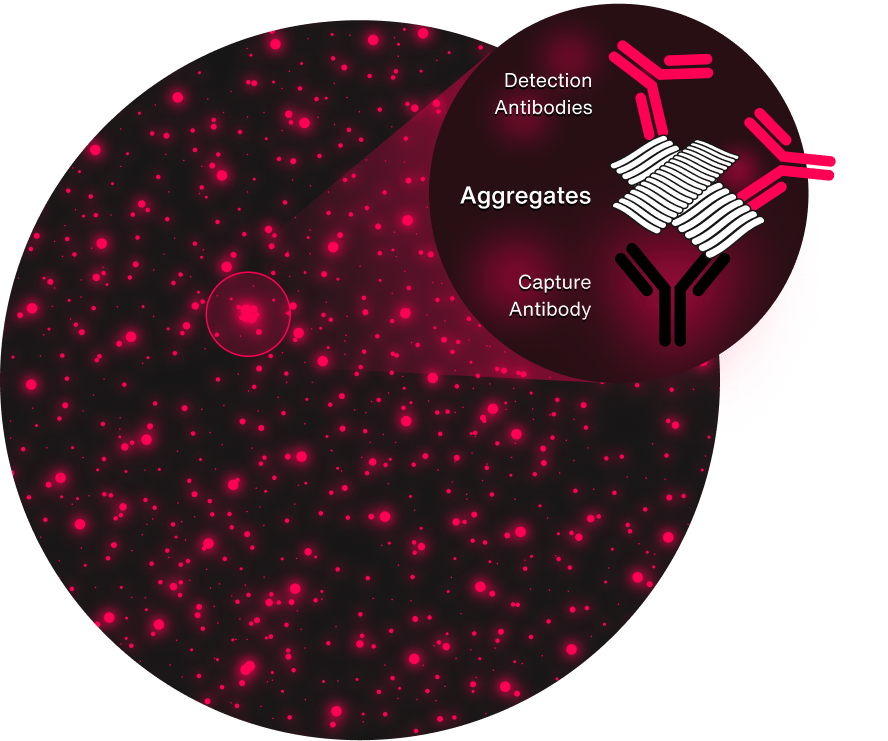
sFIDA technology
aggregates under the spotlight
The sFIDA platform integrates the precision of a selective immunoassay with the superior sensitivity of fluorescence microscopy to count single oligomers, aggregates, and particles. As a result, sFIDA can detect these biomarkers at unprecedented levels of sensitivity and specificity.
applications
we are 
attyloid is an academicy spin-off dedicated to the scientific rigor that the complex fields of protein misfolding and Central Nervous System (CNS) diseases demand. Our research plays a critical role in diagnosing and understanding these diseases and paving the way for innovative therapeutics.